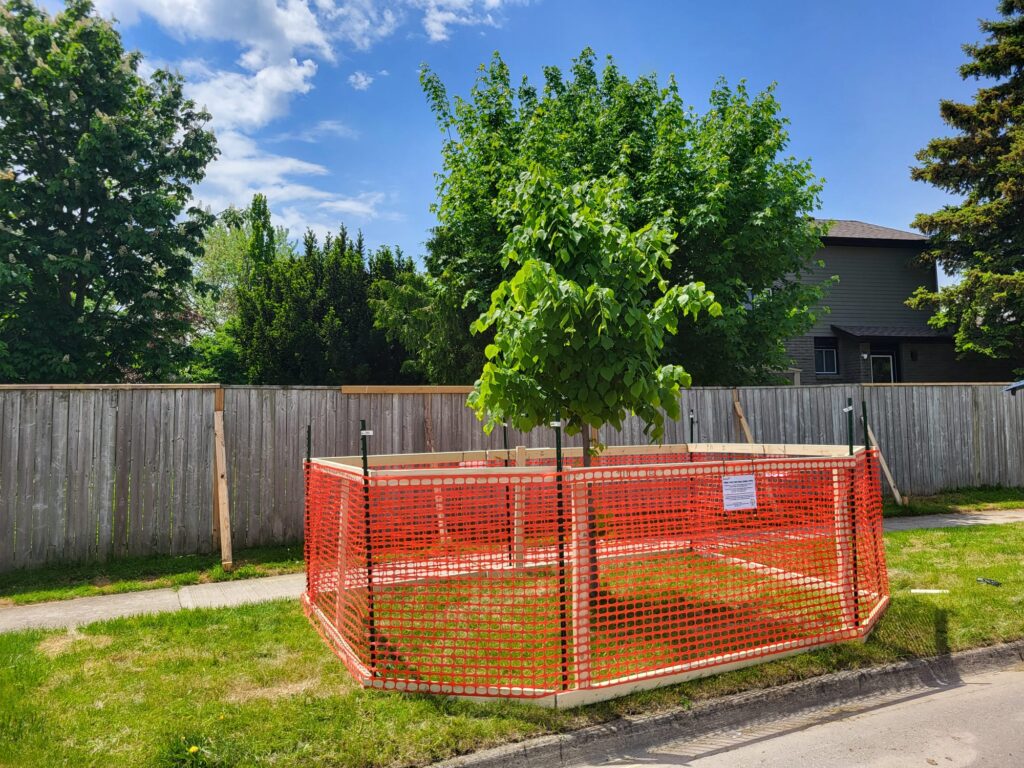
When urban construction projects intersect with nature, the trees often suffer. Ensuring the best tree protection is essential—not just for compliance with urban forestry regulations, but for safeguarding long-term environmental health. High-quality tree protection fence or hoarding is your best defense against damage caused by construction activity, weather, and even vandalism.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to protect trees on construction projects. From assessing site-specific risks to selecting the right materials to use, you’ll learn actionable steps to protect your investment and contribute to a thriving urban canopy.
Steps to Choosing the Right Tree Protection System
Step 1: Identify the threats to trees on your project
Understanding the risks specific to your construction site is the first step in choosing the right tree protection. Common threats include:
- Heavy Machinery Damage: Construction vehicles can easily harm tree trunks without proper protection and compact the soil.
- Material Storage: Heavy material inside of a Tree’s root zone compacts the soil and leads to root damage.
- Foot Traffic and Soil Compaction: High-traffic damages the soil and tree roots, and reduces tree health.
Once you’ve identified the risks, you’ll have a clear sense of the level of protection required.
Step 2: Understand urban forestry requirements
In cities like Toronto, urban forestry regulations dictate specific guidelines for protecting trees on construction sites. For example, regulations often require:
- Tree protection fencing or hoarding that meets height and durability standards. Cities usually have a specification sheet, see here for the City of Toronto’s specifications.
- Properly defined tree protection zones (TPZs) surrounding trees.
- Documentation of compliance in arborist reports completed by a certified arborist.
Working closely with a certified arborist can ensure you meet all legal requirements and avoid costly fines.
Step 3: Select the right type of hoarding
Choosing the appropriate hoarding is an important step in safeguarding trees during construction projects. The right type of protection ensures trees are shielded from potential damage caused by equipment, debris, or project activity.
- Vertical: Vertical hoarding is used to create a protective barrier around trees or sensitive forestry areas. Its primary aim is to shield trees from direct impact or damage caused by construction equipment, debris, or unauthorized access.
- Horizontal: Horizontal hoarding protects the root zone and soil around trees, particularly where excavation, heavy equipment, or foot traffic could cause compaction or damage.
- Trunk: Trunk hoarding protects the tree’s trunk from direct physical damage caused by impacts, abrasions, or collisions.
By selecting the most suitable type of tree protection—whether vertical, horizontal, or trunk-focused—you can effectively protect trees and meet environmental requirements throughout your project.
Step 4: Consider installation and maintenance needs
Tree protection barriers should be easy to install and maintain throughout the construction timeline.
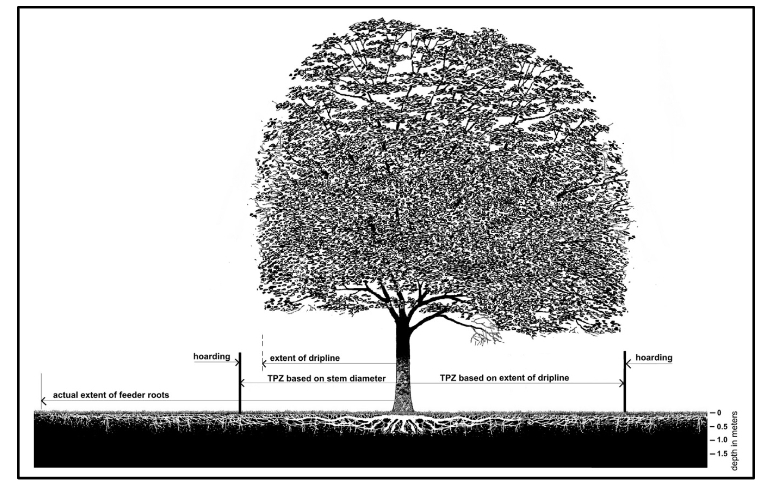
TMZ Guidelines – City of Toronto
The City of Toronto and many surrounding municipalities are very particular when it comes to tree protection. Choosing the right arborist early in the design stage can save thousands in fines, delays, and plan amendments down the road. Book an Arborist Consultation Call with Gray Matter Forestry Consulting today to ensure your project’s tree protection plan is on point.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tree protection barrier is a required step in protecting young trees on construction sites. By assessing site-specific risks, understanding regulatory requirements, and prioritising durability, you can safeguard your trees, meet compliance standards, and enhance the environmental value of your project.
At Gray Matter Forestry Consulting, we specialise in helping construction professionals protect trees efficiently while staying on track and within budget. Book an Arborist Consultation Call today to create a customised tree protection plan that works for your project.